Highly volatile economy, extreme competition and the impact of technology are forcing business owners to make changes in their workflow to stay relevant in the market. Business process automation is a strategy that leverages modern technology to improve the efficiency and productivity of your business.

We help business owners achieve growth in business productivity and revenue generation by providing consultancy and specific, tailor-made software solutions to improve the process efficiency.
We analyze your existing business process and identify areas of improvement, such as:
Identifying areas of bottleneck in the process
Identifying areas where process automation will reduce human error and decrease process time
Identifying products/solutions and vendors that can help form a better solution
Identifying the level of improvement and increase in value of the business that can be gained through BPM
We model a customized application based on our analysis after reviews and corrections. The application is developed and implemented according to the model, which increases your company’s capabilities to generate more revenue and business, while avoiding the bottlenecks and human errors that affect quality and process time. The model also leaves room for identifying, collecting and implementing evolving requirements or adjustments (user stories and artifacts) for future implementation.
We monitor our implementation of automation and hold meetings with the stakeholders to verify and gauge the level of improvement in their business post-implementation. We iron out oversights and performance tweaks and encourage feedback from end users. The feedback from end users and stake holders are collected and held in a business repository for implementation as the business grows and matures.
Check: First call resolution, customer satisfaction feedback
Check: Avg. handling time, employee error rates
Check: Avg. revenue per user / customer retention rate
Check: Cost per FTE
Operations involve manual intervention and process propegation, preventing employees from interacting with customers and building relations
Automated software with RPA reduces manual labour. Scalability is quick and easy, and results in fast response time to customer demands and helps build better customer relations
Multiple expenses such as employee salaries, maintenance of data integrety and security, marketing, advertisement, software and hardware costs reduce operational effort in maintaining customer experience
Helps in rapid internal cost reduction leading to better ROI, freeing up resources to be invested in building better customer experience
Entering and updating data, navigating multiple data sources, and retrieving relevant customer specific information becomes tedious when dealing with frustrated customers
RPA provides call center agents with the correct data at the right time allowing the agent to focus on the customer and efficiently serve his need
During calls, Agents consult their knowledgebase and various sources to provide suitable answere which takes time to read/understand while customer is on hold, and reduces customers confidence. Customer is frustrated if agent makes a human error.
RPA allows agents to identify similar problems from different users and provide instant solution thereby reducing response time and maintaining the confidence of the customer
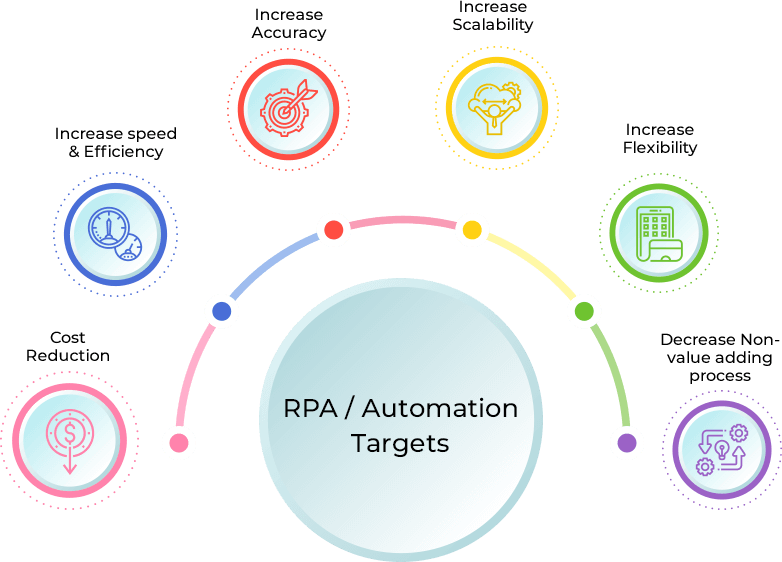
When harnessed properly, automation offers tremendous opportunities, but requires careful planning and execution to reap the benefits. A combination of domain knowledge, technology, governance structure and process expertise is essential for optimal and effective implementation of automation. The process of RPA deployment would consist of the following steps –
1
Indentify appropriate use cases which can be automated to give gains
Start with small quantifyable gains
2
Set realistic ROI goals
Standardize processes that are autometed
3
Establish Governance structure
Structuring helps set deadlines, provide guidlines and mitigate risk factors
4
Choose appropriate tools
If possible also maintain an internal team to continue the process
5
Re-engineer inefficient processes to suit automation
Aim to minimize exceptions in rules
6
Strong collaboration between business and IT is essential
Important to consider process nuances and business domain's point of view
An important step in automation is to determine which business processes would yield the highest returns when automated. Generally speaking, there are 3 process types that are good candidates for automation –
To identify processes that can be automated, we can use the following criteria as a guiding rule –
Labour intensive processes (Processes that require high FTE and so a large number of employees)
Simple Processes (Processes that have simple logic and few exceptions to rules)
Standardized Processes (Processes that deal with digitized and structured data)
On-demand Processes (Processes whose intensity needs to be able to scale up and down in short notice according to demand)
Processes Bottlenecks (Processes that are creating bottlenecks due to high time consumption)
One of the biggest challenges in implementation of automation is the time taken for ROI and overcoming the hurdles involved in automating.
Some common hurdles faced are –
Goals, expectations and suitability of automation should be driven by the consideration of these factors. Centralized tools can be used to monitor the performance and return being yielded over time to drive further decisions.
A governance structure, like the rudder of a ship helps ‘drive’ automation in the correct direction and achieve quantifiable benefits within a set period of time.
Some common hurdles faced are –
Goals, expectations and suitability of automation should be driven by the consideration of these factors. Centralized tools can be used to monitor the performance and return being yielded over time to drive further decisions.
Organizations should evaluate tools with pre-built automation libraries that have re-usable components to connect to back-end systems, data-extraction capabilities, and cost and licensing options.
There are a few leading players in the market, with the top 3 being –
Each of these tools has pros and cons and the suitability of one of these platforms, or a combination of platforms, varies based on the use case.
It is essential to understand the pros and cons of the various available tools and ‘use the right tool for the right job’.
Identification of bottlenecks and reengineering processes to make them optimal and more suitable for automation are important parts of automation implementation.
Inefficient processes with critical dependency on other processes, or processes which are not standardized and have high exception rates, would not generate the desired outcome. It is important to attempt to re-engineer these processes to make them more suitable for automation, or identify them as unsuitable candidates for automation.
The implementation of automation often fails because of lack of collaboration between Business and IT functions.
Automation is heavily dependent on IT support in structuring of data and business processes. It is equally dependent on the business’ viewpoint, domain knowledge, subject matter expertise, and in turn the nuances of business processes that need to be maintained to keep it usable. Automation should be a combined effort between the business and IT with an operating model that defines the roles and responsibilities of each player.
While the function needs to own the operational requirements, process design initiatives, and performance monitoring, aspects such as reliability, risk management, technological compatibility, identity and access control, and compliance are for the IT organization to deliver.
While the benefits of RPA might be many, businesses need a well-designed strategy to pivot from boardroom conversations to actual success. Directed systematically, RPA adoption is paving the way to achieving the cost and operational efficiencies desired by most organizations.
Businesses can also benefit from augmenting their processes using other automation techniques or specialized software, apart from just RPA robots.
AI can be used to augment and overcome some shortcomings such as nonlinear decision making and capability to handle ‘exceptions to rules’ to offer more flexibility to an automated process and reduce the requirement of manual intervention. Apart from this obvious use, AI can be further explored to augment automated processes for which some ideas could be –
Businesses can also benefit from augmenting their business processes using other automation techniques or specialized software, apart from just RPA robots.
AI can be seen as a way to transfer mundane tasks to a robot, so that human minds can be used to their full potential in doing creative and original work, instead of wasting time on sorting, organizing, responding, and reporting.
The primary drive for automation IoT is to significantly reduce operating expenditures when automation devices, sensors and actuators become Internet-enabled devices. It’s the next huge leap in productivity because there are major advantages to be derived from the acquisition and organization of previously unthinkable amounts of data. New Enterprise Manufacturing Intelligence (EMI) software brings manufacturing-related data together from many sources for reporting, analysis, visual summaries, and passing of data between enterprise-level and plant-floor systems.
We are currently working on a IoT project which is a collaboration between an Indian DTH Television provider and Over The Top media distributor, to create a universal Android based receiver box, to act both as the set top box for watching TV/Recording shows, as well as access specialized apps to watch movies/shows/videos on demand, in free, freemium (free with ads), subscription as well as pay-per-view model, with focus towards understanding the users’ viewing habits and procuring and providing content that the users want to watch.
We have outlined some generic ideas and basic methods of implementation of RPA/Automation. We can have a further, more specific discussion after we have more information on your roadmaps, views, pain points, and current status of implementation.